Intrinsically safe barrier is devices used in uncertain environments to prevent any damage by limiting electrical energy. Intrinsic safety barriers are used for environments where safety is critical, cost-effective protection is needed, space is limited, or maintenance simplicity is key.
What is Intrinsically Safe Barrier?
Intrinsically safe barriers are the devices that help control the amount of electricity going to a sensor in hazardous environments where there’s a risk of explosion. Intrinsic safety barriers limit the current, voltage, and overall energy reaching the sensor.
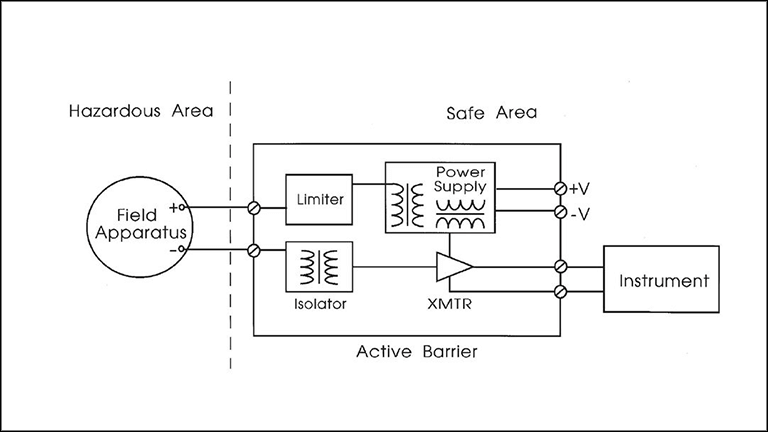
This helps stop any sparks or heat that could cause an explosion in hazardous areas or places with flammable stuff.
Intrinsically safe barriers are commonly used in various industries where there’s a risk of explosion due to flammable gasses, vapors, or dust. Some common applications include –
- Oil and Gas Industry
- Chemical Processing Plants
- Mining Operations
- Pharmaceutical Industry
- Food and Beverage Industry
- Water Treatment Plants
- Power Generation
Types of Intrinsic Safety Barriers
There are a variety of Intrinsically safe barriers serving different industries that ensure safe signal transmission in hazardous areas.
1. Isolated Safety Barrier
An isolated safety barrier is a device that keeps electrical circuits separated to prevent sparks or heat from causing explosions in hazardous areas. It makes sure that electrical energy stays in safe limits when connecting equipment in hazardous environments.
2. Zener Barrier
A Zener safety barrier is a safety device used to protect electrical circuits in hazardous environments. It works by using a component called a Zener diode to regulate voltage levels, ensuring that the electrical energy reaching equipment in a hazardous area stays within safe limits.
Essentially, it prevents excessive voltage from reaching equipment that could potentially cause sparks or ignition in flammable atmospheres.
How Does an Intrinsic Safety Barrier Work?
To avoid inflammation in hazardous areas, we have to make sure the electrical power and temperatures stay low. We need to keep the power below a certain level and the temperature from getting too high.
- For power, keep the voltage under 29 volts and the current under 300 milliamps. Or simply put power to be less than 1.3 watts. This helps prevent any sparks or heat that could cause an explosion.
- To control temperature, we use different types of intrinsic safety barriers. For example, equipment meeting the T4 class means it won’t get hotter than 135°C (275°F). It’s important because equipment giving off less than 1.3 watts usually stays below this temperature.
When To Use an Intrinsically Safe Barriers?
An Intrinsically safe barrier is used in places where there’s a risk of explosion from flammable materials like dust or gasses. These barriers are crucial in various industries like oil and gas, chemical processing and mining. These barriers help keep electrical equipment safe by limiting the amount of electricity that goes into hazardous areas.
So, if safety is a big concern and you’re working in a place where there’s a chance of explosions, using an intrinsic safety barrier is a smart move.
How To Install Intrinsic Safety Barrier?
Setting up an intrinsically safe barrier is easier compared to installing explosion-proof enclosures. But, it’s not just about buying certified equipment like pressure sensors or load cells. The whole system needs to be designed to be intrinsically safe.
This means documenting all the parts and wiring used in the system. After installation, there will be inspections to make sure everything’s working right. These inspections happen regularly to check for any damage or if any parts have been replaced without approval.
Normally, electrical inspections include tests for insulation and grounding. But with intrinsic safety systems, these tests might not work the same way. If needed, it’s best to get advice from experts.
Benefits Of Using Intrinsic Safety Barrier
Using intrinsic safety barriers for electrical equipment in hazardous environments has many benefits:
- It helps keep the workplace safe, preventing explosions and protecting everyone nearby.
- It’s cheaper and less bulky than using explosion-proof enclosures. You can save additional money if you use regular cables.
- Easy for maintenance and fixing problems without stopping work.
- It reduces the risk of accidents, insurance premiums might be lower, saving money in the long run.
Things To Consider While Using Intrinsic Safety Barrier
When using intrinsic safety barriers, remember to:
- Check for certification
- Make sure all components work together
- Follow installation guidelines
- Keep good documentation
- Inspect regularly for damage
- Train staff properly
- Test the system periodically
- Seek expert advice when needed
Choosing The Right Intrinsic Safety Barrier
When choosing intrinsic safety barriers, you need to check their specs and approvals. You have to consider things like operating temperature and how many channels they support. Also, consider the maximum voltage and current they can handle without causing problems. You’ll find devices that limit both AC and DC currents, or just one of them. These factors help ensure the barrier works well with your equipment and keeps everything safe.
By considering these factors in detail, you can select the right intrinsic safety barrier that meets your requirements and provides reliable protection in hazardous environments.
Conclusion
In conclusion, intrinsically safe barriers are essential safety devices used in hazardous environments to prevent explosions by limiting electrical energy. They are deployed in industries such as oil and gas, chemical processing, and mining, where the risk of ignition is high. It’s crucial to use intrinsic safety barriers when safety is a top priority, cost-effective protection is needed, space is limited, or maintenance simplicity is essential.
By implementing intrinsic safety barriers effectively, organizations can ensure the safety of personnel and equipment while minimizing the risk of ignition in hazardous areas.

